Zen Project #1: A Web Site and a New Technology to Help People Scale the Web
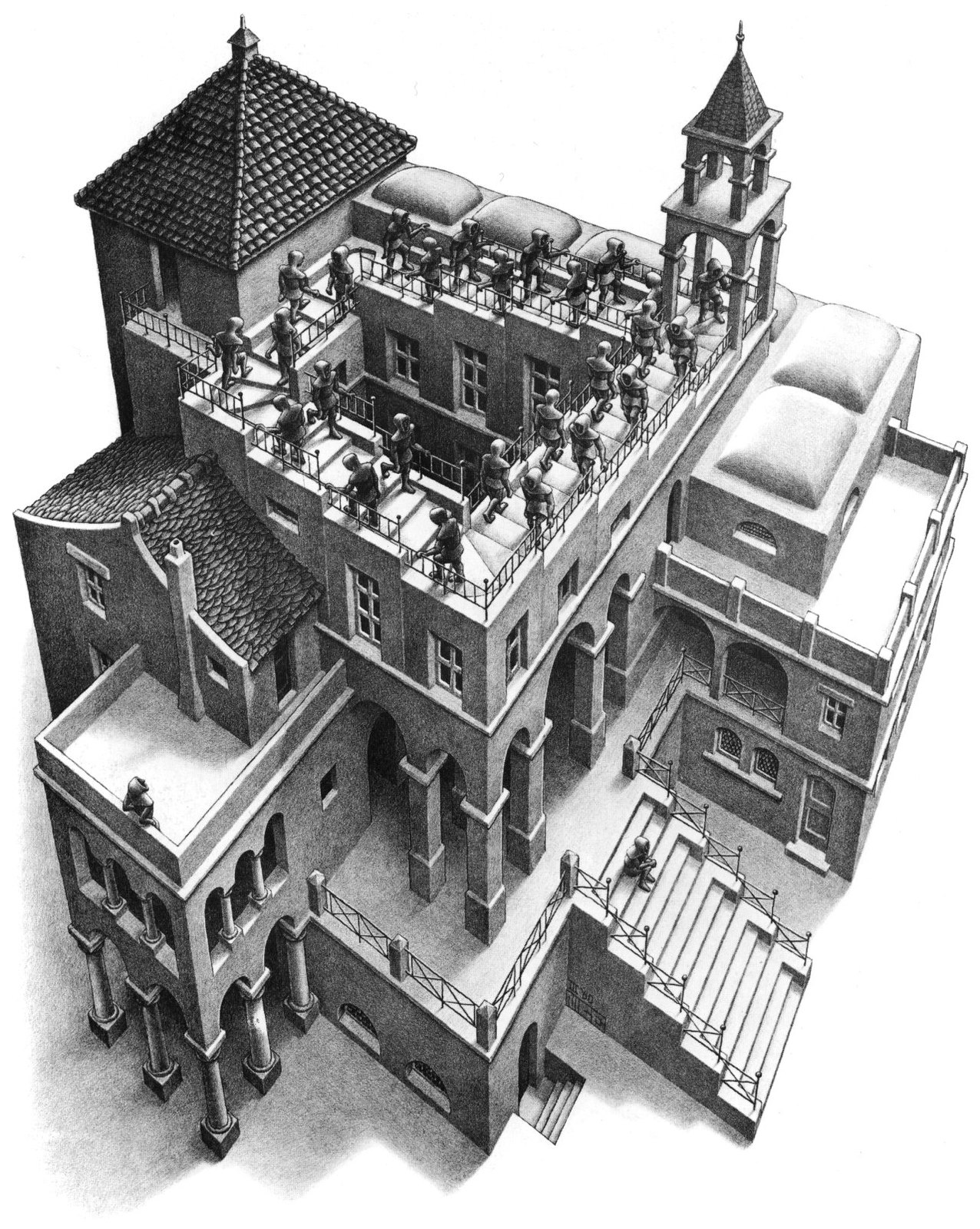
Ascending and Descending, M. C. Escher, 1960
In this, the first in a series of articles on Zen, I describe a large and general problem people have as users of the web. Then I describe a set of technologies I am working on, more fully described at Mashweb.Club and my older website, tomelam.com, which I call Zen, that could significantly reduce the problem. On average, each of us consumes three times as much information as we did in 1960 and checks 40 web sites a day, according to a 2010 article on National Public Radio’s web site. New York Times articles tell us that this makes us impatient, forgetful, anxious, shallow, and unfocused. Information is our crack cocaine, and we should have been in rehab long ago. An information fix is even called a hit! (See below.)
Part of the problem is the difficulty in finding what we seek—even when we know it is on the web. When we search for something on the web, we hope that the process will be linear and finite, but we get lost in a strange loop, a tangled hierarchy of searching, scanning, surfing, and subscribing that we try to climb down like a staircase. In our search for digital nirvana, employing bookmarks, tags, annotations, hyperlinks, search, indices, rankings, ratings, and subscriptions, we find ourselves skipping up and down between various levels of metadata and web resources, like the monks trudging endlessly on the paradoxical, looped staircase in Escher’s lithograph “Ascending and Descending,” shown above. On our way we collect scores of bookmarks and piles of paper notes, and get a headache and short temper, too.
Let us try to outline the stages or hierarchies of the most general search:
- Search for an answer to a question using a general purpose or specialized “search engine,” typically by entering keywords, phrases, and parameters (e.g., date, tags, domain, URL, links-to, similar-to). Items that match the query criteria are called hits. Hits are presented in lists or in hierarchical outlines and are typically ordered by criteria such as relevance or paid placement. Searching is optional if we can replace the list or outline of hits with a list or outline of resources from categories in a web directory. Examples of directories of the whole web were the now-defunct Yahoo! Directory and DMOZ. (See Wikipedia’s entries on Yahoo! Directory and DMOZ and a successor to DMOZ.) Many specialized directories of web resources also exist.
- Examine brief descriptions, summaries, or snippets of the items in the list or outline, if available.
- Open the links to the relevant-looking hits—in new windows or tabs if possible. Evaluate these linked-to resources for fitness to our purpose.
This linear procedure can often miss highly specialized information. Sometimes this happens because we weren’t able to choose the best search query at the outset: we didn’t have enough information to choose well. Sometimes we might not even know information is available pertaining to our problem. And sometimes we really need information from the “deep web,” i.e., data available only behind a form-oriented user interface, such as an airline fare search interface or a phone directory search interface. The “deep web” is generally not indexable by web search engines (“spiders” to be more precise). A better alternative to this hit-and-miss search technique is “semantic search”. (When I first wrote this article in 2010, it was sometimes called “idea search,” but the source I referred to then is now gone, not even archived on Archive.org.) The following articles provide a start at learning about semantic search:
- SearchEngineJournal.com’s article “Semantic Search: What It Is & Why It Matters for SEO Today”.
- SearchEngineWatch.com’s article “The beginner’s guide to semantic search: Examples and tools”.
- Wikipedia.org’s article “Semantic search”.
- OnCrawl.com’s article “What is semantic SEO?".
- Google’s article Google Knowledge Graph Search API.
- Stewart, Scott, and Zelevinsky’s article “Idea Navigation: Structured Browsing for Unstructured Text”.
- Adam Westerski’s book Semantic Technologies in Idea Management Systems: A Model for Interoperability, Linking and Filtering.
We often resort to trial-and-error variations of our search, but this is usually frustrating. A better approach than the trial-and-error, hit-or-miss approach is to refine each level of hierarchy, as described above, by applying the whole search procedure to that level. That is, we seek information resources, meta-resources (e.g., search engines), and methods of search. A method of search can involve subscription to a forum, wiki, mailing list, social bookmarking service (like Delicious, being slowly revived, archived here; and Digg; and Reddit; and Pinboard), or general social media (like Twitter and Facebook) so that we can make new friends and acquaintances (or communicate with old friends) and get help from them. Or it might be to subscribe to pertinent blogs in an attempt to find out which experts are sharing helpful information on our topic. (Try Feedly or read about Google Reader. Also read about Google Blog Search or try Bloglovin, or QuiteRSS, or some of the sites in this moreofit list.) The “helpful information” could be the final solution we are seeking, or it could be a set of new keywords we hadn’t considered or known, or it could be some other forum, wiki, blog, mailing list, chat room, or other resource. The results on topic-specific forums, wikis, blogs, mailing lists, and chat rooms will be pre-filtered by design, avoiding completely irrelevant hits that can swamp the relevant ones in a general-purpose whole-web search engine. There are many other strategies for refining the levels of search hierarchy.
Other problems arise in our research on the web and in remembering what we find: too many web pages and no adequate means of keeping track of them. If we open a window for each web page that looks pertinent to our search, we soon overburden our web browser or our operating system. The browser will crash, or, in the case of Google Chrome, tab panes will crash. Web browsing will slow to a desperate crawl. (These problems with Google Chrome, the most-used web browser, have existed for for a decade or more. Chrome has some of the best support for extensions and developer support, so it is hard to replace.) If we bookmark our web pages, we irretrievably lose time navigating the browser’s bookmark manager and anyway might not be able to find the bookmarks later when we need them.
So what’s the answer, short of a very heavyweight “idea browser” and possibly much better natural language processing—even artificial sentience—that is not within our reach? I propose we make it possible to write the web as easily as desktop text documents can be written, and to implement some of the original ideas about hypertext like transclusion, so one single web page becomes our notebook and scrapbook. The reader might think of Evernote, Google Notebook, or Xanadu, but the kernel of the technology I’m working on focuses on organizing and tuning the user’s view of and interaction with the web and on being universally usable, globally, by anyone with a reasonably up-to-date web browser, without browser plug-ins. On top of the kernel, many web-server-assisted capabilities can be built.
Zen will allow the user to get close to the process of refining his searches, so that he can keep meta-resources, final results, and records of how he got results at his fingertips, under his control, programmed via a simple visual interface. He should be able to program the Internet by dragging and flowing links, text, data in microformats, and media from any web page into a web page he controls and saves to a web server, and via simple programming of his own interface to the web. He should be able to use his links as bookmarks. He should be able to organize the links, text, and media in folders, tab panes, accordion panes, and other web widgets and lazy-load them so that time is not taken when he re-opens his page at a later date. Only the open pages or other widgets that contain the links, text, data, and media should be loaded. (That’s how a lazy-loaded pane works.) Zen will even allow lazy-loaded widgets to be put into other lazy-loaded widgets. Many of the web-server-assisted services mentioned above and below can easily be codified and automated so that they can be included as widgets on a web page.
The user will be able to share these pages over the web with other people very easily, in many ways. The special web server will serve his web page and will use its in-built proxy capabilities to enable the user’s web page to be composed of content from multiple web sites. Such a composition is called a mashup. The JavaScript inside the user’s web page will enable many kinds of mashup to be created even without help from the special web server. These JavaScript-enabled mashups will use certain kinds of mashable content from multiple web sites. Microformats, mentioned above, can assist the mashups to “digest” and pour content from disparate places into the page. For example, much social media, including the present blog, can be accessed via web feeds using an RSS or Atom microformat. This allows the media to be formatted by a news aggregator for human consumption or inserted into a web page.
Various features of Zen will allow development of a web page to proceed smoothly. Someday maybe the web server will enable the user’s web navigation to be recorded automatically. Variations of the user’s web page will be as easily produced as Git branches, because a Git-like “filesystem” on the web server will record the components of the web page analogously to Git commits. The system must be easy to understand without much training.
I am beginning to program Zen to enable this writable web. I plan eventually to create a web site offering registrations for people to create their own portals to the web. These will be real portals: most of the media content in the web pages will be hot-linked, not copied. For web sites that disallow hot-linking, the special web proxy will be used to work around the limitation by imitating web browsers that such web sites expect to deal with. I am hoping that many people will be interested in the technology, and I am seeking collaborations from companies, investors, technology marketing experts, and programmers.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Glad to hear it! Please tell us how we can improve.
Sorry to hear that. Please tell us how we can improve.